Describe the Liquid State According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory
Move rapidly in a constant random motion d. The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior.

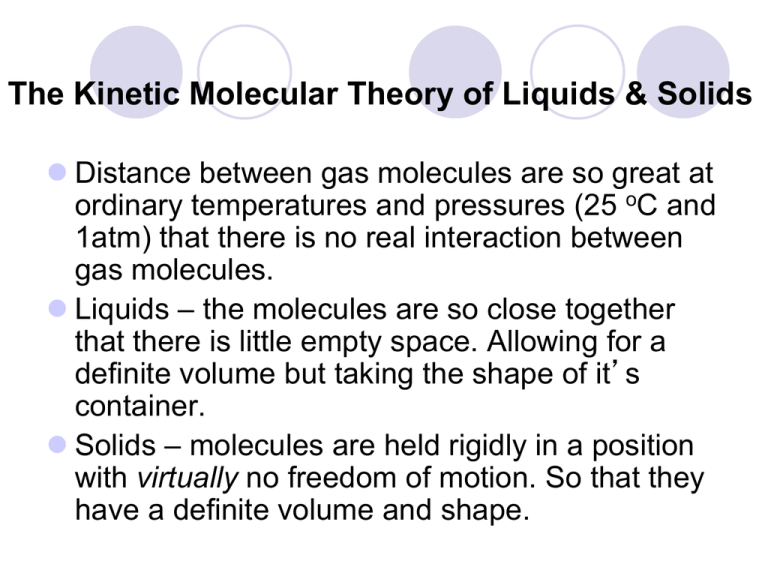
Kinetic Molecular Theory And Liquids And Solids Ppt Video Online Download
Lose kinetic energy when colliding 4.
. Identify each statement as True or False. The kinetic molecular theory suggests that the vapor pressure of a liquid depends on its temperature. This in turn determines whether the substance exists in the solid liquid or gaseous state.
In order to understand my answer my answer you must have the basic knowledge of KMT Kinetic Molecular Theory Well according to KMT. The kinetic theory of matter also helps us to understand other properties of matter. According to the kinetic-molecular theory of liquids the particles are not bound together in fixed positions.
Because of their close proximity to one another liquid and solid particles experience intermolecular forces. As can be seen in the graph of kinetic energy versus number of molecules the fraction of the molecules that have enough energy to escape from a liquid increases with the temperature of the liquid. Solid liquid and gas and how matter can change from one phase to the next.
Every particle has energy however the amount of energy changes based on the temperature of the matter sample. The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that. The liquid state has molecules that are close together but not locked in place as in a solid.
The Kinetic Molecular theory is used to describe the behavior of gas. Broadly the kinetic theory of matter says that all matter is composed of particles. These forces keep particles close together.
Liquids The particles of a liquid possess a greater amount of kinetic energy than the particles of a solid. This in turn determines whether the substance exists in the solid liquid or gaseous state. The examples of kinetic theory include Brownian Motion the random movement of dust particles because of collisions with air molecules and how gases behave ie.
32 The kinetic molecular theory ESAAL The kinetic theory of matter helps us to explain why matter exists in different phases ie. According to the basic assumption of kinetic molecular theory gas particles. All particles have energy but the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in.
When particles in the liquid phase are heated they gain kinetic energy and move faster and further apart. The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their. The state of the substance is then determined by whether it is solid liquid or gaseous.
Liquid The particles are arranged disorderly and less closely packed than in solid. Describe the liquid state according to the kinetic-molecular theory. See full answer below.
Solid liquid and gas and how matter can change from one phase to another. 1- Liquids have a high density relative to gases. Solids have the strongest intermolecular forces gases the weakest Intermolecular Forces 1.
What is the kinetic molecular theory of liquids. The attractive forces between particles is stronger than in gases but weaker than in solids. Up to 24 cash back figure 8.
How does the kinetic molecular theory explain the liquid properties of relatively high density ability to diffuse and ability to evaporate. Matter is made up of particles that are constantly moving. Describe the liquid state according the the kinetic molecular theory.
According to the kinetic-molecular theory of liquids the particles are not bound together in fixed positions. All particles have energy but the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in. All particles have energy but the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in.
The molecules in a liquid are attracted to each other. Boyles Charles and Gay-Lussacs Laws. Matter is made up of particles that are constantly moving.
It is important to realise that what we will go on to describe is only a theory. What is the abbreviation for kinetic molecular theory. However the kinetic energy of particles is low.
List the properties of liquids. Instead they move about constantly giving them their fluidity. The kinetic theory of matter also helps us to understand other properties of matter.
Gas particles are in. According to the kinetic molecular theory of matter The particles that makeup matter are continually moving. When a substance increases in temperature heat is being added and its particles are gaining kinetic energy.
Also this theory explains how temperature affects the states of substancesNov 4 2014. According to the Kinetic-Molecular theory the state of a substance depends on the attractive forces between the molecules of the substance. Matter is made up of particles that are constantly moving.
The kinetic theory of matter helps us to explain why matter exists in different phases ie. The process by which particles escape from the surface of a nonboiling liquid and enter the gas state Pg 363 Q. Have a significant volume with respect to the volume of the container they occupy c.
Thus the particles of liquid will not be in an ordered arrangement and will take on the shape of the container that they are placed in. 1 Describe the liquid state according to the kinetic-molecular theory. The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that.
Describe kinetic molecular theory. There are three basic types. This in turn determines whether the substance exists in the solid liquid or gaseous state.
Are far apart b. Thus they are able to slide over one another. The kinetic molecular theory of matter states that.
These particles will possess enough energy to flow throughout a container and past one another. Gas The particles are arranged disorderly and very far apart. Liquids have more kinetic energy than solids.
Gasses consist of large number of tiny particles that are far apart as compared to their size. Instead they move about constantly giving them their fluidity List the properties of liquids. It gives the relationship between pressure temperature and kinetic energy.
An example of evaporation in a liquid Questions 1. Eventually they have enough energy to escape the forces of attraction holding them together in the liquid phase and they move very fast and far from each other and exist in the gaseous phase.

Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter States Of Matter Molecular Ideal Gas Law

The Kinetic Theory Of Matter Kinetic Theory Matter Science States Of Matter
Comments
Post a Comment